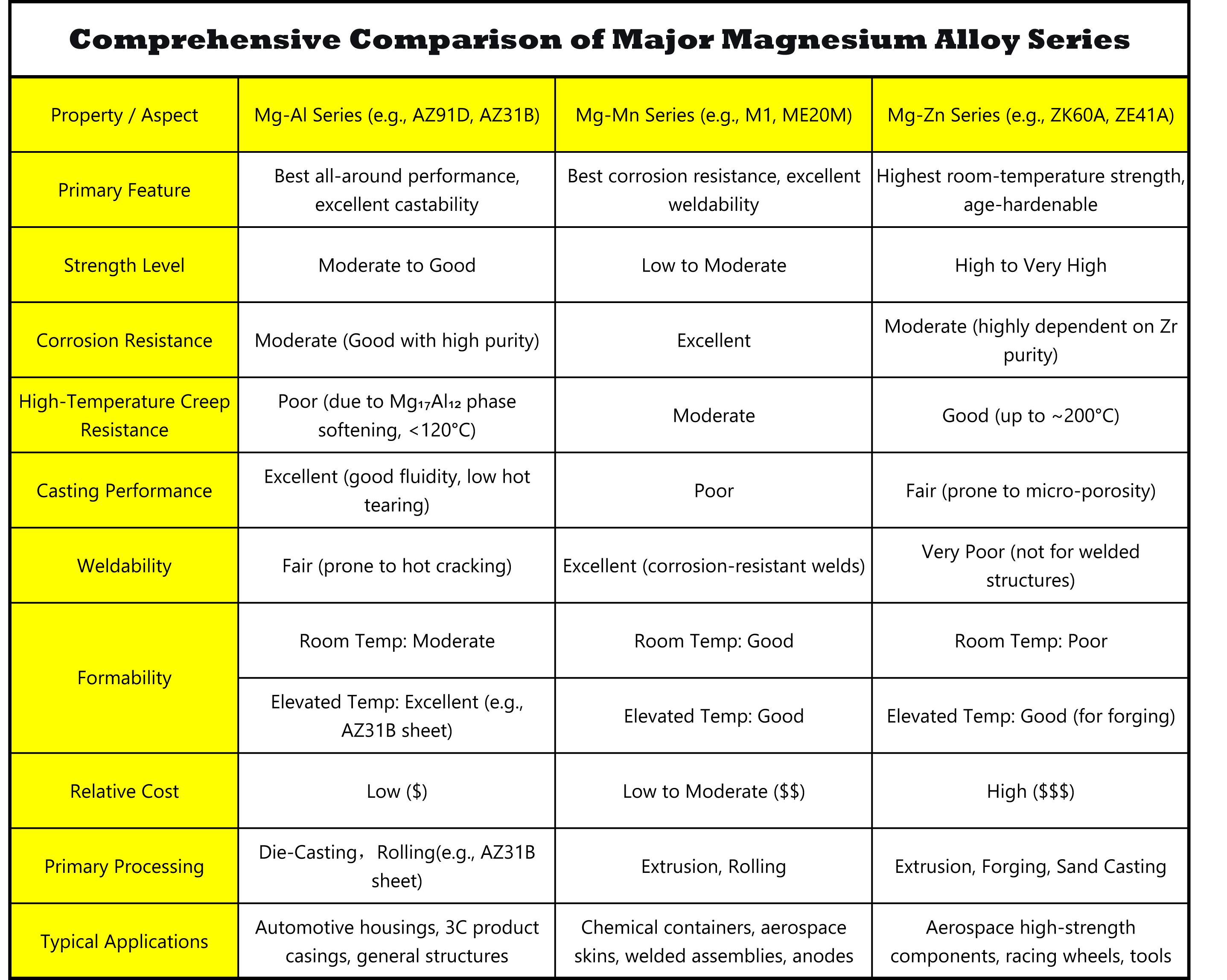
Magnesium alloys are primarily categorized based on their major alloying elements. The main systems are Mg-Al, Mg-Mn, Mg-Zn, and Mg-RE, each offering a unique set of properties tailored for specific applications.

Mg-Al Alloys
Key Characteristics:
⭐Advantages:
Excellent Castability & Fluidity: Ideal for
high-pressure die-casting of thin-walled, complex parts (e.g., electronic housings)
Good Room-Temperature Strength: Offers the best combination of strength and ductility among common cast Mg alloys.
High Cost Performance: Mature, economical manufacturing processes.
⭐Limitations:
Poor Creep Resistance: Prone to
deformation under sustained load at elevated temperatures (>120°C).
Moderate Corrosion Resistance: Requires high-purity grades (e.g., AZ91D) for adequate performance.
Common Grades:
⭐AZ91D: The industry standard for die-casting. Offers a superb balance of strength, castability, and corrosion resistance.
⭐AZ31B: It offers good strength, ductility, and formability.Good ductility, suitable for wrought processes, moderate strength.
⭐AM60B / AM50A: Provide higher ductility, impact toughness, and energy absorption. Used in automotive safety components.
Typical Applications:
Automotive: Transmission cases, clutch
housings, steering wheels, seat frames, intake manifolds.
3C Electronics: Laptop cases, mobile phone frames, camera bodies.
Industrial & Consumer Goods: Power tool housings, lawnmower components.
Why Choose Mg-Al Alloys?
Select Mg-Al alloys for high-volume production of complex die-cast components where the optimal balance of strength, weight, and cost is critical.
Mg-Mn Alloys
Key Characteristics:
⭐Advantages:
Outstanding Corrosion Resistance: Superior resistance to saltwater and other corrosive environments, among the best of all Mg alloys.
Excellent Weldability and Formability: Can be easily welded,extruded, and stamped.
Moderate Creep Resistance: Better
than Mg-Al systems, though still limited.
⭐Limitations:
Low to Moderate Strength: Mechanical
strength is generally lower than Mg-Al and Mg-Zn systems.
Poor Casting Characteristics: Not
suitable for die-casting.
Common Grades:
⭐ME20M: It offers one of the best corrosion resistance performances among all commercial magnesium alloys, with excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking. It welds very well, and weld zones are resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for fabricated structures.
⭐M1A: Essentially pure magnesium with a manganese addition. The benchmark for corrosion resistance.
⭐M2S (Mg-2%Mn): A slightly stronger variant of M1.
Typical Applications:
Corrosion-Resistant Structures: Chemical tanks, piping, components for marine environments.
Aerospace: Aircraft skin panels, non-load-bearing internal structures.
Consumer Goods: Luggage frames, sports equipment (e.g., archery bows).
Why Choose Mg-Mn Alloys?
Choose Mg-Mn alloys when the primary design requirements are extreme corrosion resistance and excellent formability/weldability, and high mechanical strength is not the main concern.
Mg-Zn Alloys
Key Characteristics:
⭐Advantages:
High Strength and Yield Ratio: Can achieve the highest strength levels of common Mg alloys through heat treatment (T5,T6 tempers).
Good Creep Resistance: Better high-temperature stability than Mg-Al alloys.
⭐ Limitations:
Poor Castability: High hot-tearing susceptibility, making them unsuitable for standard die-casting.
Moderate Corrosion Resistance: Requires protective coatings.
Higher Cost: Due to Zr content and more complex processing.
Common Grades:
⭐ZK60A: The premier high-strength wrought
Mg alloy. Widely used in extrusions and forgings.
⭐ZE41A: Contains rare earth elements (RE) to improve castability and elevated temperature properties.
⭐ZK61M:ZK61M is one of the strongest commercially available magnesium alloys.It is one of the primary magnesium alloys used for forging, exhibiting good plastic deformation capability when heated.Due to its high zinc content and age-hardening nature, ZK-series alloys have very poor weldability.
Typical Applications:
High-Stress Structural Components: Bicycle frames, motorcycle wheels, automotive racing components.
Aerospace: Helicopter gearbox housings, aircraft fittings, missile parts.
Sports Equipment: High-performance
bicycle components, baseball bats, climbing gear.
Why Choose Mg-Zn Alloys?
Select Mg-Zn alloys for applications demanding the highest specific strength
(strength-to-density ratio), where performance justifies higher material and processing costs. Ideal for critical, high-stress components.
Mg-RE Alloys
Key Characteristics:
⭐Exceptional High-Temperature Performance: Retains superior strength and outstanding resistance to creep (deformation under load) at temperatures ranging from 150°C to 300°C, a critical advantage over most other Mg alloys.
⭐Superior Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Offers an excellent balance of very high strength and low density, both at room and elevated temperatures.
⭐Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Certain rare earth elements (e.g.,Neodymium) promote the formation of a more stable and protective surface film, improving durability in harsh environments.
⭐Good Castability: Exhibits low hot tearing tendency and good fluidity, making them suitable for producing complex, high-integrity castings.
⭐Premium Cost: Rare earth elements are strategic materials with volatile pricing, placing Mg-RE alloys in the high-end, premium material category.
Common RE Elements & Their Effects:
⭐Neodymium (Nd): A cornerstone RE element. It significantly enhances room and high-temperature strength, creep resistance, and corrosion performance. It is the key element in WE series alloys (e.g.,WE43).
⭐Yttrium (Y): Greatly improves creep resistance and high-temperature strength. It is often added in combination with other RE elements like Neodymium.
⭐Gadolinium (Gd): Provides potent solid solution strengthening, drastically increasing high-temperature performance. It is the primary element in ultra-high-strength Mg-Gd-based alloys.
⭐Cerium (Ce) / Lanthanum (La): Often added as a low-cost mixture called Mischmetal. Improves castability and high-temperature creep resistance, though with less strengthening effect than Nd or Y.
Primary Alloy Series & Applications:
⭐Mg-Y-Nd Series (e.g., WE43, WE54)Description: This is the most renowned and widely used Mg-RE alloy series, representing the pinnacle of magnesium technology. WE43 can typically operate continuously at temperatures up to 250°C.
Common Grades: WE43 (Mg-4Y-3Nd-0.5Zr), WE54 (Mg-5Y-4Nd-0.5Zr)
Processing: Primarily used for casting (sand,investment) and extrusion.
Applications:
Aerospace: Engine gearboxes, helicopter transmission housings, aircraft door and seat frames.
Racing & High-Performance Automotive: Gearbox and clutch housings, engine brackets.
Defense: Radar housings, missile components.
⭐ Mg-Nd Series(e.g., ZE41, QE22)
Description: Alloys containing Neodymium and Zinc, offering good castability and moderate strength, particularly at elevated temperatures. corrosion resistance is superior to traditional AZ series alloys.
Common Grades: ZE41 (Mg-4Zn-1Nd-0.5Zr), QE22 (Mg-2Ag-2Nd-0.5Zr)
Processing: Primarily used for casting.
Applications: Aircraft generator housings, engine accessory gearboxes, helicopter rotor system components.
⭐Mg-Gd-Y Series (Ultra-High-Strength Alloys)
Description: This newer generation of ultra-high-strength Mg-RE alloys utilizes high additions of Gadolinium (Gd) and Yttrium (Y).Through specific heat treatment, these alloys can achieve strength levels comparable to some aluminum alloys, making them a key focus of current research.
Common Grades: VW94 (Mg-9Gd-4Y-0.5Zr), GW103 (Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.5Zr)
Processing: Suitable for both casting and wrought processing (extrusion, forging).
Applications: Critical aerospace structural components, spacecraft parts, and high-end racing chassis where extreme weight reduction and strength are mandatory.
